Honey Harvesting in Nepal a Unique Tradition of Gurungs
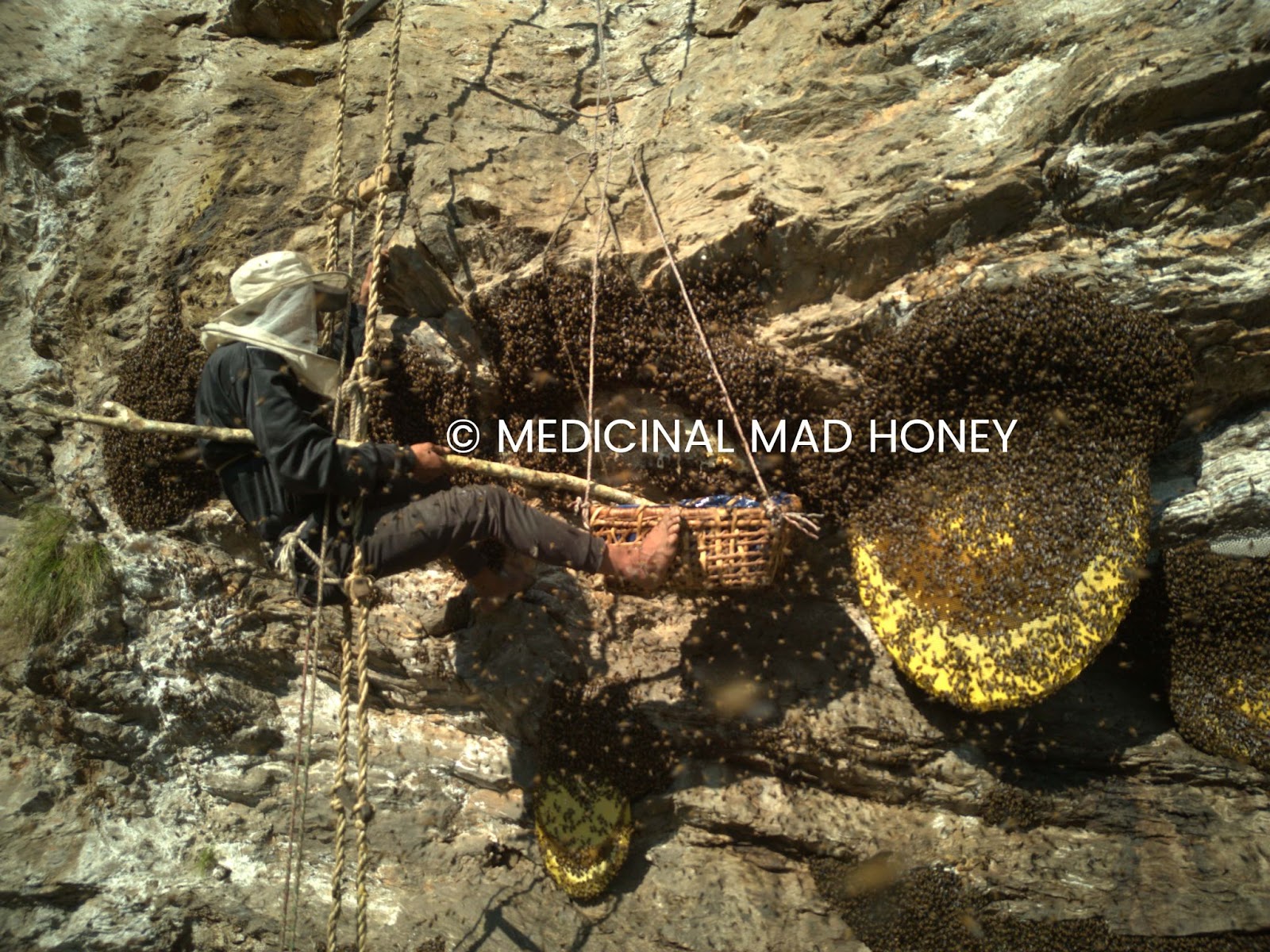

The Himalaya runners of the Nepal House an ethnic group, Gurungs, which maintains a traditional but old practice of honey harvest. These ethnic groups across Nepal have been increasing dangerous heights for centuries to collect wild honey, which lives in the world’s largest honeybee species, APIS Laboriosa, traditionally as Himalaya -Riesenhoneybee. This traditional practice is carried out in order to make a living with religious devotion and extensive natural wisdom and at the same time take serious risks.
The traditional practice
The activities for the Honig Assembly in Nepal are mainly carried out by Gurung and some Magar, Lepcha families from central -nepal together with Lamjung, Kaski, Jajarkot and Manang districts. The honey collectors lead their climbs to access Cliffside beehives twice a year in spring and autumn. Honey hunters in Nepal, whose local name is “Honey Hunters”, climb with handmade cable ladders and bamboo poles while hanging hundreds of foot in the air.
This practice stands up due to its religious interventions. Before each honey meeting, the community carries out prayer rituals with victim offers in order to obtain the consent of the forest spirit for a safe harvest that achieves good results. The harvesting process requires trained hunters from early childhood who have proven their expertise in practice.

The crazy honey itself
The honey extracted from the forest is completely different from what people find in standard market locations. The intoxicating crazy honey from the nectar of rhododendron flowers consists of the presence of gray anotoxins that have psychoactive properties. The traditional use of this honey in light amounts for the treatment of high blood pressure and diabetes and anxiety is still in practice in the community. A greater consumption of the substance leads to hallucinations and at the same time causes toxic reactions in the entire body.
The international market has developed interest in buying Mad Honey, which means that it becomes a valuable raw material worldwide. Modern demand for Mad Honey has created economic prospects for local population groups, although inadequate availability, rarity and over -harvesting have an impact on sustainable production.
Challenges and maintenance
The cultural tradition of honey hunt in Nepal slowly decreases and there is afraid of the extinction of these bees. The population groups of bees are exposed to suitable habitats due to environmental changes as well as the deforestation and loss. The number of qualified honey hunters has decreased because young people prefer urban employment towards traditional practices.
Together with organizations such as medical Mad Honey, local communities are now working with local communities to teach sustainable harvesting methods and provide security lessons and to spread information about the importance of bee habitats for ecology. Ecological tourism companies are now helping to observe tourists on how to observe the honey harvest activities and at the same time achieve additional local income.
A cultural treasure
The practice of honey harvest in Nepal is more than the collection of natural sweeteners, hallucinogenic liquid and recreation elixir. This tradition lives today when it expresses the seamless unity between humans and its natural environment. The challenge for Nepal is to defend its timeless wisdom by contemporary economic changes that occur in the modernization of progress. The preservation of honey use depends on the combined support and nature conservation work, which will support the tradition in its role as a symbol for the legacy of Nepal.